Can inflammation cause weight gain? As a registered dietitian, I often get asked this by my clients who struggle with inflammation and want to lose excess weight. Inflammation is your body’s natural response to injury or infection and is your immune system’s way of waving a red flag, signaling that something needs attention.
And yes, inflammation can cause weight gain, but there’s more to it.
There are two main types of inflammation: acute and chronic.
Acute inflammation is short-term, like when you cut your finger or catch a cold. It’s your body’s way of healing and protecting itself. Chronic inflammation, on the other hand, lingers over a longer period, sometimes for months or years.

How does inflammation play a role in weight gain?
Understanding this connection is important, especially if you’re trying to manage your weight and improve your overall health. In this blog post, we’ll dig into the relationship between inflammation and weight gain, explore the science behind it, and provide practical tips on how to decrease inflammation to support your weight loss journey.
Let’s get started!
Understanding Inflammation
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is your body’s natural defense mechanism. When working with my clients, I often find that understanding the differences between acute and chronic inflammation is important for effective management.
- Acute Inflammation: This is the immediate and short-term response your body has to injury or infection. Think of the redness and swelling you see when you get a cut, or the fever you experience during a cold. Acute inflammation is essential for healing – it’s your body’s way of fighting off harmful invaders and starting the repair process.
- Chronic Inflammation: Unlike its acute counterpart, chronic inflammation lingers over a longer period, sometimes for months or years. It can be caused by persistent infections, prolonged exposure to irritants, or autoimmune disorders where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. Chronic inflammation is less obvious and can silently contribute to various health issues, including weight gain, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
The immune system plays a crucial role in the inflammatory response. When the body detects a problem, it sends out white blood cells to the affected area to protect and heal it. While this process is beneficial and necessary in acute inflammation, continuous immune responses in chronic inflammation can lead to tissue damage and contribute to long-term health problems.

The Link Between Chronic Inflammation and Weight Gain
Does Inflammation Cause Weight Gain?
Yes, chronic inflammation can contribute to weight gain. When your body is in a state of chronic inflammation, it’s constantly fighting a low-level battle. This ongoing immune response can lead to various changes in your body that promote weight gain.
Research has shown that chronic inflammation can interfere with your body’s ability to regulate metabolism and insulin sensitivity. For example, inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) have been found at higher levels in individuals with obesity. These markers are not just indicators of inflammation but also play active roles in disrupting normal metabolic processes.
One study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found a strong association between higher levels of inflammatory markers and increased body fat. The study suggested that inflammation might lead to weight gain by altering the way the body stores and processes fat.
Why Does Inflammation Cause Weight Gain?
There are several mechanisms through which chronic inflammation can lead to weight gain:
- Metabolic Changes: Chronic inflammation can disrupt normal metabolic processes, making it harder for your body to burn calories efficiently. This means you might gain weight even if you’re not eating more than usual.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Inflammation affects hormones like insulin and cortisol. Insulin resistance, a common consequence of chronic inflammation, can cause your body to store more fat. Elevated cortisol levels, often associated with stress and inflammation, can also lead to increased fat storage, particularly around the abdomen.
- Inflammatory Cytokines: These are proteins released by immune cells during the inflammatory response. Certain cytokines, like tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and IL-6, can promote fat storage and interfere with the signals that regulate appetite and satiety, making it harder to maintain a healthy weight.
Understanding these mechanisms shows just how important it is to manage inflammation to manage your weight and improve your health.
Inflammation and Weight
Fluid Retention and Inflammation
Inflammation can cause your body to hold onto extra water, leading to fluid retention. This is particularly noticeable in chronic inflammation, where the body’s prolonged immune response can lead to swelling and puffiness. When tissues retain fluid, it can add to your overall weight, making the number on the scale go up.
This fluid retention can also affect how you perceive your weight gain. You might feel heavier or notice that your clothes fit tighter, even if you haven’t gained fat. This can be frustrating and confusing, especially if you’re trying to lose weight.
Obesity and Inflammation
The Cyclical Relationship Between Obesity and Inflammation
Obesity and inflammation are intertwined in a vicious cycle. Excess body weight can lead to chronic inflammation, and chronic inflammation can make it more challenging to lose weight, creating a frustrating loop.
When you carry excess weight, especially around the abdomen, your body stores more fat cells, known as adipocytes. These fat cells don’t just sit idle; they actively produce inflammatory substances called adipokines.
Adipokines, such as TNF-alpha and IL-6, contribute to a state of low-grade, chronic inflammation. This ongoing inflammatory response can then disrupt your metabolic processes, making it harder to burn calories and easier to gain weight.

How Excess Weight Contributes to Chronic Inflammation
Carrying excess weight increases the burden on your body in multiple ways:
- Increased Adipose Tissue: More fat tissue means more adipokines are produced, perpetuating inflammation.
- Stress on the Body: Excess weight puts additional stress on your joints, muscles, and organs, which can lead to more inflammatory responses as your body tries to cope with this extra load.
- Immune System Overload: Persistent excess weight can strain your immune system, making it less efficient at managing inflammation and other bodily functions.
The continuous production of inflammatory markers by excess fat can keep your body in a constant state of alert, exacerbating chronic inflammation and its associated health risks, such as cardiovascular disease and insulin resistance.
Weight Gain Triggers Leptin Resistance
Leptin is a hormone produced by fat cells that helps regulate appetite and energy balance. In a healthy state, leptin signals to your brain that you have enough energy stored and don’t need to eat more. However, in individuals with obesity, this signaling can go awry.
When you gain weight, your fat cells produce more leptin.
Over time, high levels of leptin can lead to leptin resistance, where the brain no longer responds to the hormone’s signals effectively. This can result in a constant feeling of hunger and reduced energy expenditure, further promoting weight gain.
Leptin resistance is closely linked to inflammation.
Inflammatory cytokines can interfere with leptin signaling, exacerbating leptin resistance and creating another feedback loop where inflammation and weight gain fuel each other.
Breaking this cycle involves addressing both the increased weight gain and the underlying inflammation through a combination of diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
Reducing inflammation can help improve leptin sensitivity, support your weight loss goals, and enhance overall health.

Insulin Resistance and Its Connection to Inflammation
Insulin resistance occurs when your body’s cells become less responsive to the hormone insulin, which is responsible for regulating blood sugar levels. As a result, your pancreas produces more insulin to compensate. Over time, this can lead to higher insulin levels in the blood, which is not only a marker for potential diabetes but also a contributor to chronic inflammation.
Chronic inflammation and insulin resistance are closely linked. When your body is in a state of chronic inflammation, it can disrupt the normal functioning of insulin, leading to insulin resistance. Conversely, insulin resistance can promote inflammation, creating a vicious cycle that makes it difficult to break free from either condition.
Inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) are often elevated in individuals with insulin resistance. These markers indicate that the body’s immune system is constantly activated, which can damage tissues and organs over time. The continuous state of inflammation can further impair insulin signaling, making it harder for cells to absorb glucose, thus perpetuating insulin resistance.

How Managing Insulin Resistance Can Aid in Reducing Inflammation and Weight
Managing insulin resistance is vital for reducing inflammation and achieving sustainable weight loss. Here are some effective strategies to help you manage insulin resistance:
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in whole foods, fiber, and healthy fats can improve insulin sensitivity. Focus on consuming plenty of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid refined carbs, sugary foods, and trans fats, which can exacerbate insulin resistance and inflammation.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity by increasing glucose uptake by muscles. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, most days of the week. Resistance training can also be particularly effective in improving insulin sensitivity.
- Weight Management: Losing excess weight can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation. Focus on sustainable weight loss through mindful eating and regular exercise rather than quick fixes or fad diets.
- Stress Reduction: Chronic stress can worsen insulin resistance and inflammation. Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your daily routine, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature.
- Quality Sleep: Poor sleep can negatively affect insulin sensitivity. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to support overall health and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Medications and Supplements: In some cases, medications or supplements may be necessary to manage insulin resistance. Speak with your healthcare provider about options like metformin, which can help improve insulin sensitivity, or supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids and magnesium, which have been shown to support metabolic health.
For more detailed strategies on managing inflammation and insulin resistance, check out this helpful article at EatingWell.
By addressing insulin resistance, you can reduce inflammation, support weight loss, and improve your overall health. Making these changes can break the cycle of inflammation and insulin resistance, paving the way for a healthier, more balanced life.
Diet and Inflammation: What You Need to Know
Diet plays a big role in managing and reducing inflammation. What you eat can either fuel the fire of chronic inflammation or help extinguish it. Making informed food choices is a powerful way to support your body’s natural defenses and promote overall health.
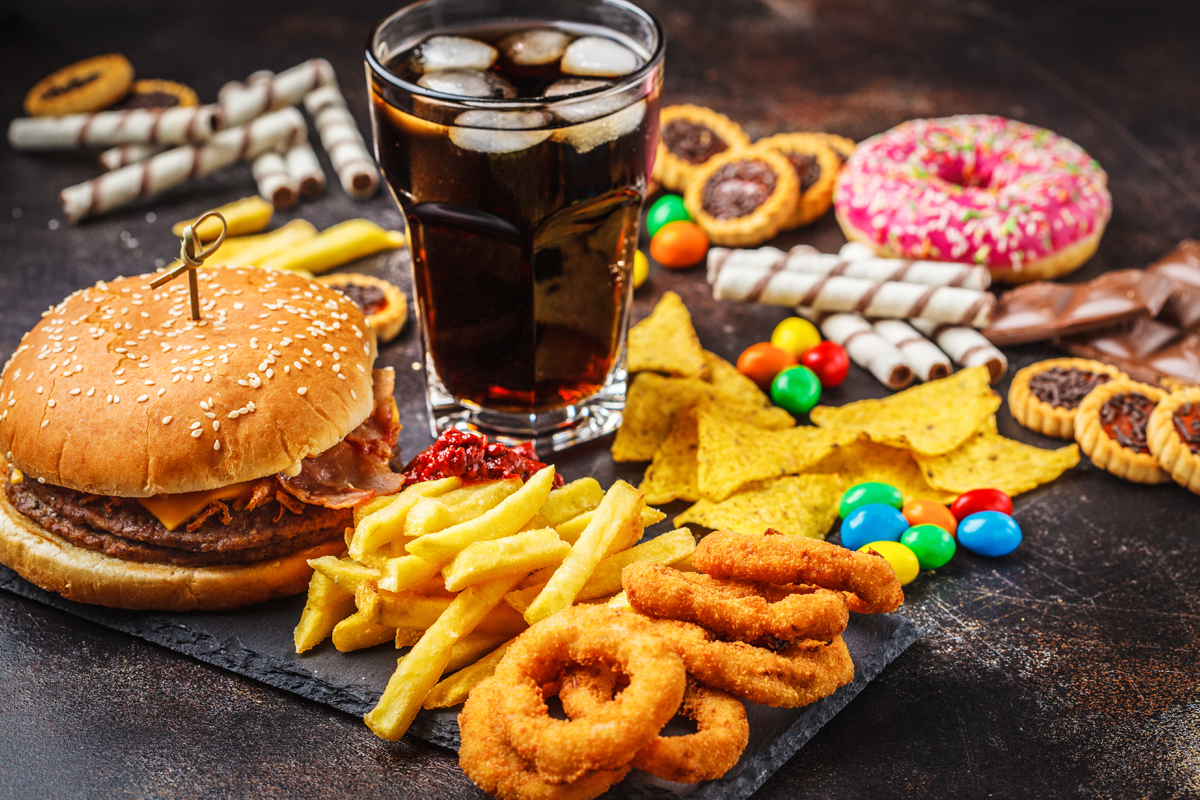

Foods That Cause Inflammation
Certain foods are known to contribute to inflammation in the body. Understanding which foods to avoid can help you manage and reduce chronic inflammation.
- High-Sugar Foods: Foods high in sugar can spike your blood sugar levels and lead to an increase in inflammatory markers. Sugary snacks, sodas, and processed foods are major culprits. High sugar intake can also contribute to weight gain and fuel inflammation.
- Refined Carbohydrates: Foods like white bread, pastries, and many breakfast cereals are high in refined carbs. These foods can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels, promoting inflammation.
- Processed Meats: Meats like bacon, sausages, and deli meats contain high levels of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which are inflammatory compounds formed when meat is cooked at high temperatures.
- Trans Fats: Found in many fried foods, baked goods, and margarine, trans fats can increase inflammation and are linked to an increased risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease.
- Excessive Alcohol: While moderate alcohol consumption can have some health benefits, excessive intake can lead to a rise in inflammatory markers and negatively affect your health.
To help curb those sugar cravings and take a step towards reducing inflammation, consider downloading my Sugar Cravings PDF for tips and strategies to manage and reduce your sugar intake.
Foods That Fight Inflammation
Many of my clients have found success with incorporating anti-inflammatory foods into their diet to reduce inflammation and support overall health. Scientific research supports the benefits of these foods in lowering inflammatory markers and promoting overall well-being. I encourage you to give some of these a try and see how they can make a difference in your health.
Here are some key foods to consider:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in antioxidants and fiber, fruits and vegetables help combat oxidative stress and inflammation. Berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and Brussels sprouts are particularly beneficial.
- Healthy Fats: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (like salmon and mackerel), chia seeds, and walnuts, have powerful anti-inflammatory effects. Olive oil, especially extra virgin, is another excellent source of healthy fats.
- Whole Grains: Unlike refined grains, whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats are high in fiber and nutrients that can help reduce inflammation.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are packed with anti-inflammatory properties and provide a good source of healthy fats and protein.
- Spices and Herbs: Turmeric, ginger, garlic, and cinnamon are known for their anti-inflammatory properties. Including these in your meals can boost both flavor and health benefits.
- Tea: Green tea and herbal teas like chamomile are rich in antioxidants and have anti-inflammatory properties.

Benefits of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Adopting an anti-inflammatory diet can offer numerous health benefits, including:
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: Lowering inflammation can reduce the risk of chronic conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
- Improved Metabolic Health: Managing inflammation can help improve insulin sensitivity and metabolic function, making it easier to manage weight.
- Enhanced Mental Health: Some studies suggest that reducing inflammation can improve mood and cognitive function, contributing to better mental health.
An anti-inflammatory diet is not just about avoiding certain foods but also about incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense, whole foods that support your body’s natural ability to heal and thrive.
Try incorporating anti-inflammatory recipes like the Brown Rice Shrimp Bowl with Tomatoes and Avocados (below), or a Kale and Quinoa Salad with Lemon Dressing. These meals are packed with nutrients and flavors that support your health. For more inspiration, check out this collection of anti-inflammatory dinner recipes.
Recipe: Brown Rice Shrimp Bowl with Tomatoes & Avocado
This Brown Rice Shrimp Bowl is not only delicious but also packed with anti-inflammatory ingredients that can help you feel your best.
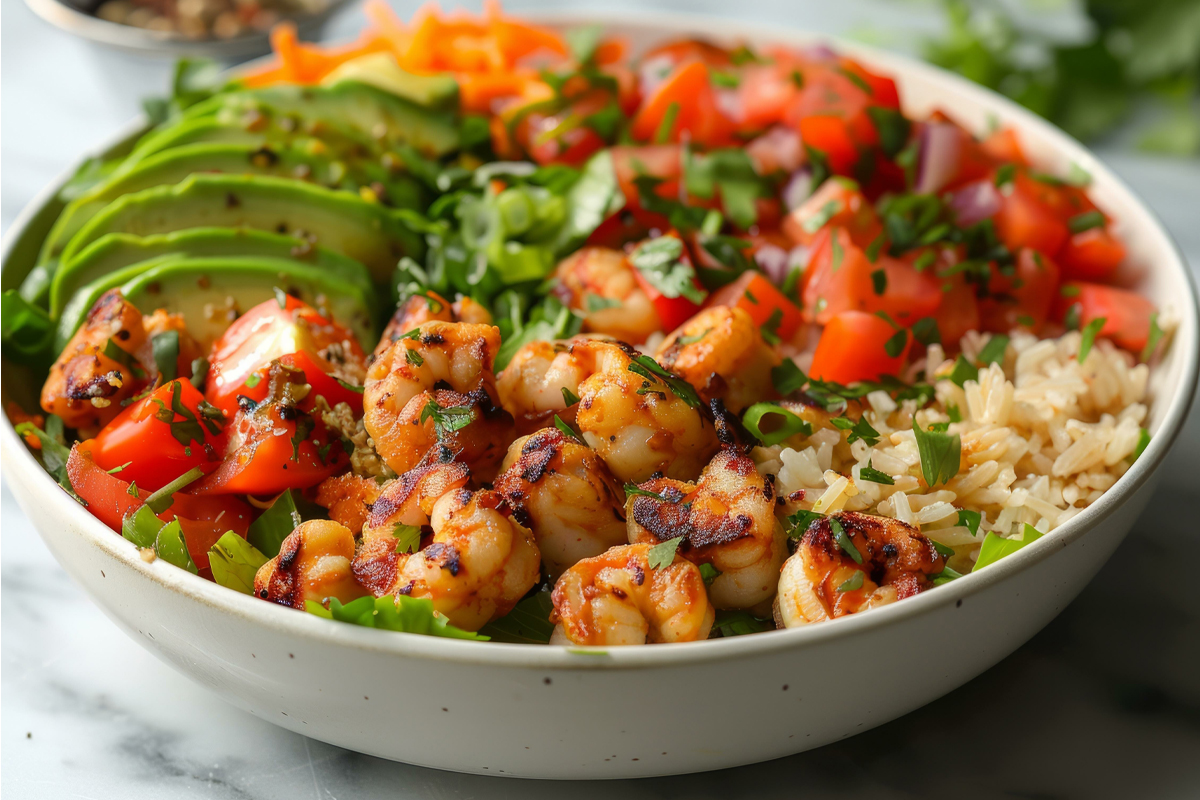

The combination of brown rice and shrimp provides a satisfying and nutrient-rich base, while the ginger-sesame sauce adds a burst of flavor. Topped with juicy tomatoes and creamy avocado, this bowl is loaded with antioxidants and healthy fats that support weight management and reduce inflammation. Plus, it’s quick and easy to prepare, making it a perfect choice for a wholesome meal on busy days. You can even use leftover brown rice or opt for pre-cooked rice to save time.
- Prep Time: 30 mins
- Total Time: 30 mins
- Servings: 4
Ingredients
- ¾ cup thinly sliced scallion greens
- ¼ cup reduced-sodium tamari
- 1 ½ tablespoons mirin (or rice wine)
- 1 ½ tablespoons toasted (dark) sesame oil
- 1 tablespoon white sesame seeds
- 2 teaspoons grated fresh ginger
- ½ teaspoon crushed red pepper (Optional)
- 12 ounces cooked shrimp, cut into 1/2-inch pieces
- 2 cups cooked brown rice
- 2 tablespoons rice vinegar
- 2 cups sliced cherry tomatoes
- 2 cups diced avocado
- ¼ cup chopped cilantro
- ¼ cup toasted black sesame seeds
Instructions:
- Whisk scallion greens, tamari, mirin, oil, white sesame seeds, ginger and crushed red pepper, if using, in a medium bowl. Set aside 2 tablespoons of the sauce in a small bowl. Add shrimp to the sauce in the medium bowl and gently toss to coat.
- Combine rice and vinegar in a large bowl. Divide among 4 bowls and top each with 3/4 cup shrimp, 1/2 cup each tomatoes and avocado, and 1 tablespoon each cilantro and black sesame seeds. Drizzle with the reserved sauce and serve.
Source: EatingWell.com
For more tips on incorporating an anti-inflammatory diet, check out my post on the Mediterranean Diet, which is a great example of an anti-inflammatory eating plan.

How to Get Rid of Inflammation Weight
Strategies to Reduce Inflammation and Promote Weight Loss
Reducing inflammation is key to promoting weight loss and improving overall health. Here are some effective lifestyle changes to help you combat chronic inflammation:
Lifestyle Changes
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce inflammation and improve your metabolic health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, such as walking, swimming, or cycling, most days of the week. Exercise not only helps with weight management but also boosts your immune system and reduces stress levels.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can contribute to inflammation and weight gain. Incorporate stress-reducing practices into your daily routine, such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, or simply spending time in nature. Finding ways to relax and unwind can significantly lower your inflammation levels.
- Quality Sleep: Poor sleep can increase inflammation and affect your weight. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Establish a regular sleep routine, create a restful environment, and avoid screens before bedtime to improve your sleep quality.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated helps your body function optimally and can reduce inflammation. Drink plenty of water throughout the day and limit sugary drinks and excessive caffeine. A rule of thumb is to drink half your weight in water!
Reducing inflammation through these lifestyle changes can help you achieve a healthier weight and improve your overall well-being. Remember, it’s not just about losing weight but also about creating a sustainable, healthy lifestyle that supports your body’s natural defenses.

Wrapping It Up: Your Path to Reduced Inflammation and Better Health
As a registered dietitian, I have seen firsthand the benefits of a holistic approach to managing inflammation. Managing inflammation is not just about addressing a single aspect of your lifestyle; it’s about creating a holistic approach that incorporates diet, exercise, stress management, and quality sleep.
By understanding the complex relationship between inflammation and weight gain, you’re better equipped to make informed decisions that support your overall health.
Key Takeaways
- Understand Inflammation: Recognize the difference between acute and chronic inflammation and how each impacts your body.
- Identify Triggers: Be mindful of foods and lifestyle factors that can contribute to inflammation, such as high-sugar foods, processed meats, and chronic stress.
- Adopt Anti-Inflammatory Habits: Incorporate anti-inflammatory foods into your diet, engage in regular physical activity, manage stress effectively, and ensure you get quality sleep.
- Address Insulin Resistance: By improving insulin sensitivity through diet and lifestyle changes, you can break the cycle of inflammation and support sustainable weight loss.
- Holistic Approach: Remember, it’s not just about losing weight but creating a balanced lifestyle that promotes long-term health and well-being.
Your Next Steps
Ready to take control of inflammation and enhance your health journey? Start by incorporating the tips and strategies discussed in this blog. Download the Sugar Cravings PDF to help manage your sugar intake, and try out some anti-inflammatory recipes like the Brown Rice Shrimp Bowl with Tomatoes and Avocados or a Kale and Quinoa Salad with Lemon Dressing.
Sugar Cravings PDF Download
Want more support?
For personalized guidance, book a complimentary consultation to discuss your specific health needs and create a tailored plan to reduce inflammation and achieve your health and weight loss goals.
Every small step you take towards reducing inflammation is a step towards a healthier, happier you!






